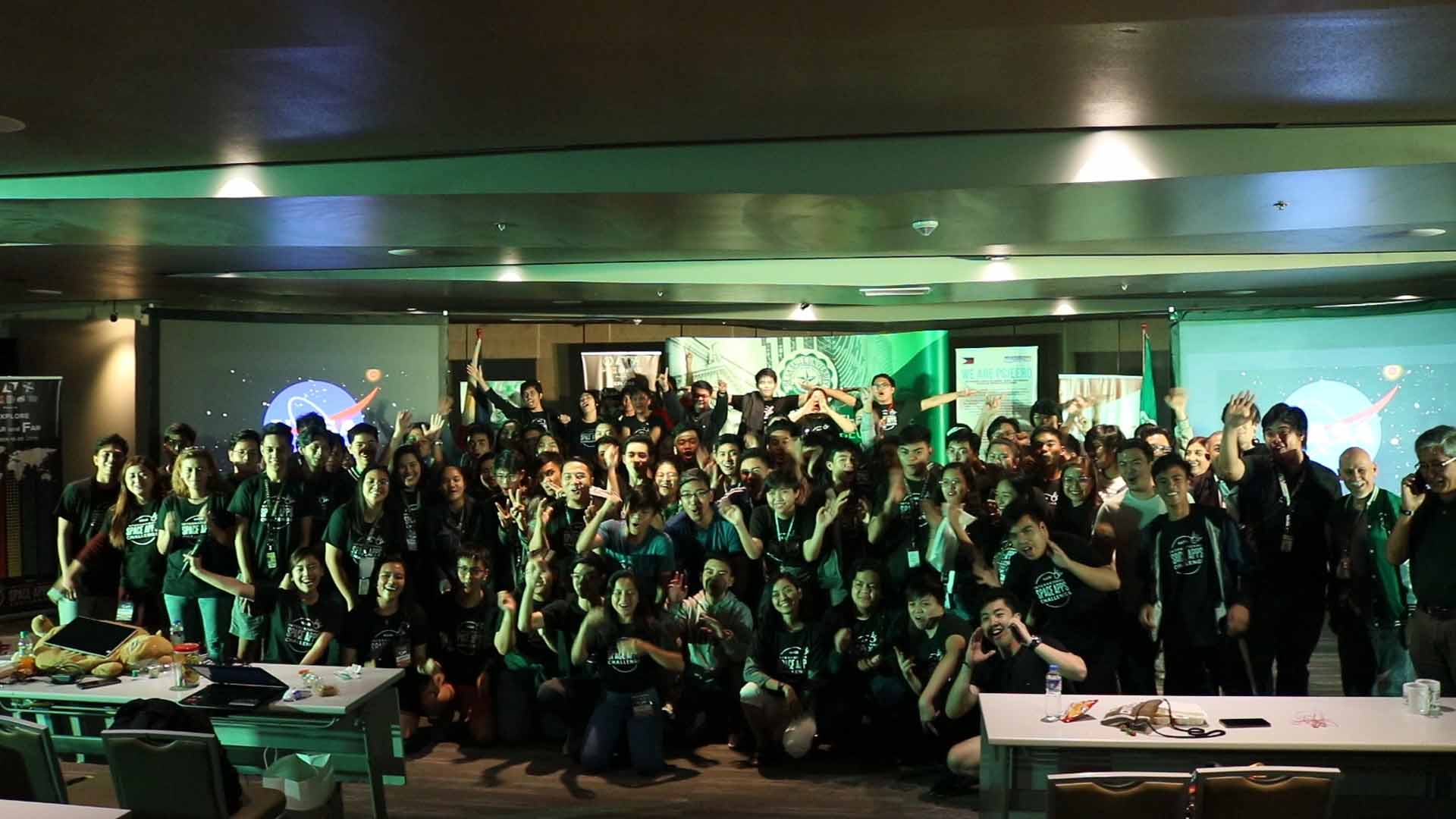
A deployable, autonomous ocean waste collection system utilizing space data to locate nearby garbage patches built by students from De La Salle University and an automated information portal which correlates dengue cases with real-time data from satellite, climate, and search engines won the National Aeronautics and Space Administration’s International Space Apps Challenge last October 18-20, 2019 in Manila, in collaboration with the Philippine Council for Industry, Energy and Emerging Technology Research and Development of the Department of Science and Technology (DOST-PCIEERD), Animo Labs technology business incubator, PLDT InnoLab, American Corner Manila, the U.S. government, and part of the Design Week Philippines with Department of Trade and Industry-Design Center of the Philippines.

Using NASA’s Ocean Surface Current Analysis Real-time (OSCAR) data to determine possible locations of ocean garbage patches using GPS, PaWiKAN uses a pair of deployable, dynamically reconfigurable boats capable of trapping and returning ocean waste back to ground. It is equipped with extended-range radio system based on LoRa technology and Arduino to communicate with sensors and controlled by a deployment station. It was developed by Lasallian electronics and communications engineering students Samantha Maxine Santos, Antonio Miguel S. Alejo, Grant Lewis Bulaong, and Janos Lance L. Tiberio of Ocean’s 4, who also joined the last year’s hackathon, creating a hyper-casual puzzle game utilizing images from the Hubble Space Telescope and intuitive physics concepts.
“Our global bodies of water are actually littered with plastics. This is a very futuristic solution to help get rid of plastics currently floating or submerged in global waters. It is timely and relevant solution,” according to Monchito B. Ibrahim, Industry Development Committee Chairman of the Analytics Association of the Philippines and former undersecretary of the Department of Information and Communications Technology.

With 271,480 dengue cases resulting in 1,107 deaths as reported from January 1 to August 31, 2019 by the World Health Organization, the Aedes Project team composed of Dominic Vincent D. Ligot, Mark Toledo, Frances Claire Tayco, and Jansen Dumaliang Lopez developed a forecasting model of dengue cases using climate and digital data and pinpointing possible hotspots from satellite data. Correlating information from Sentinel-2 Copernicus and Landsat 8 satellites, DOST-PAGASA for climate, and trends from search engines, potential dengue hotspots will be displayed in a web interface. Indices like Fraction of Absorbed Photosynthetically Active Radiation (FAPAR) and Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI) are used in identifying areas with green vegetation while Normalized Difference Water Index (NDWI) to identify areas with water. Combining these indices reveal potential areas of stagnant water capable of being breeding grounds of mosquitoes.
“It benefits the community especially those countries suffering from malaria and dengue, just like the Philippines. I think it has a global impact. This is the new science to know the potential areas where dengue might occur. It is a good app,” said Engr. Raul C. Sabularse, deputy executive director of DOST-PCIEERD.
“It is very relevant to the Philippines and other countries which usually having problems with dengue. The team was able to show that it’s not really difficult to have all the data you need and integrate all of them and make them accessible to everyone for them to be able to use it. It’s a working model. It is something can actually be made usable in a short span of six months,” Mr. Ibrahim said.
Space Apps leader Dr. Paula S. Bontempi, the acting deputy director of the Earth Science Mission, NASA’s Science Mission Directorate was impressed of these solutions presented in Manila, “The top two are really good. There were definitely a few projects right behind them. There is a lot of good talent out there. It was nice to see.”
Rex Lor from United Nations Development Programme in the Philippines commended the use of the Sustainable Development Goals on Good Health and Well-Being, and Life Below Water of the winning solutions showcasing the “pivotal role of cutting-edge digital technologies in the creation of strategies for sustainable development in the face of evolving development issues.”
Both champions will join teams around the world to be evaluated by NASA to approximately select the top 30 projects as global finalists in early December, and the top six winners will be announced in January 2020. Winners shall be invited to visit the NASA’s Kennedy Space Center at Florida in 2020.
Last year, team iNON used a citizen science platform by NASA to develop an application seeking to communicate scientific data to fishermen even without Internet connection, which led them to victory as the first Pinoy global winner. Their project called ISDApp is currently being incubated by Animo Labs.

University president Br. Raymundo B. Suplido FSC hopes that NASA Space Apps would “encourage our young Filipino researchers and scientists to create ideas and startups based on space science and technology, and pave the way for the promotion and awareness of the programs of our own Philippine space agency.”
Vice President Leni Robredo recognized Space Apps as a platform “where some of our country’s brightest minds can collaborate in finding and creating solutions to our most pressing problems, not just in space, but more importantly here on Earth.”
“Space Apps is a community of scientists and engineers, artists and hackers coming together to address key issues here on Earth. At the heart of Space Apps are data that come to us from spacecraft flying around Earth and are looking at our world,” as explained by Dr. Thomas Zurbuchen, NASA associate administrator for science.
#SpaceApps #SpaceAppsPH